- Home
- /
- Analytics
- /
- Stat Procs
- /
- How is Somers' D calculated in PROC LOGISTIC?
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Lets say we want to calculate Somers' D (SD) on the following data:
data have;
x = 1; y = 1; output;
x = 1; y = 1; output;
x = 1; y = 0; output;
x = 0; y = 0; output;
x = 1; y = 1; output;
run;According to the definitions in the wiki article the following can be observed:
concordant pairs = 3
discordant pairs = 0
tied pairs = 3
all pairs = 10
Given these results, SD would be equal to (3 - 0)/(10 - 3) = 0.4285
Now if we execute the PROC LOGISTIC procedure we get the following:
proc logistic data=have;
model y = x;
run;
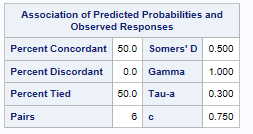
The results show a different value for SD. In addition if 50% of the pairs are tied, which means that the total number of pairs according to the output is equal to
6 + 6*0.5 = 9, which is incorrect.
Can someone please explain to me what I am missing?
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
All of the statistics in the "Association of Predicted Probabilities and Observed Responses" table can be computed as shown in this note. As noted in the Details: Model Fitting Information: Rank Correlation of Observed Responses and Predicted Probabilities section of the LOGISTIC documentation where these statistics are defined, each pair of observations must have differing responses. So, there are 6 pairs, not 10.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
All of the statistics in the "Association of Predicted Probabilities and Observed Responses" table can be computed as shown in this note. As noted in the Details: Model Fitting Information: Rank Correlation of Observed Responses and Predicted Probabilities section of the LOGISTIC documentation where these statistics are defined, each pair of observations must have differing responses. So, there are 6 pairs, not 10.
ANOVA, or Analysis Of Variance, is used to compare the averages or means of two or more populations to better understand how they differ. Watch this tutorial for more.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.