- Home
- /
- Programming
- /
- Programming
- /
- Read in XLS files without PROC IMPORT or XLSX engine
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
I'm trying to read in just the first row of 100+ XLS files (to get the list of var names).
PROC IMPORT will not work because the data are very messy and it would take too long to sort through (when I try this I get a lot of, X variable has been defined as both char and numeric).
XLSX engine not a good bet because each of the 100+ files has a distinct sheet name and there's no way to impute it.
This is what I have so far. It reads in the first row of each file with no bad log messages, but the text is nonsense:
data pre_process_&i.;
infile "&&fnm&i.."
delimiter=',' missover dsd lrecl=32767 firstobs=1 obs=1;
informat
header1 $2500.
;
input
header1 $
;
run;
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If they only have one sheet then just use proc import.
Example:
proc import datafile='file1.xls' dbms=xls out=dummy replace;
run;
proc contents data=dummy noprint out=contents;
run;
proc print data=contents;
var varnum name label;
run;
To aggregate the names over multiple XLS files you could make a macro that takes as input the filename and appends each new file to base table.
%macro xls_vars(filename);
proc import datafile=&filename dbms=xls out=dummy replace;
run;
proc contents data=dummy noprint out=contents;
run;
data this_file;
length filename $200 ;
filename=&filename;
set contents(keep=varnum name label);
run;
proc append base=all_files data=this_file force;
run;
%mend;Then call it once for each XLS file.
So if you have a dataset name FILES with a variable named FILENAME that has the list of XLS files you want read you could run this step to call the macro once for each file.
data _null_;
set files;
call execute(cats('%nrstr(%xls_vars)(',quote(trim(filename),"'"),')'));
run;
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Do you have actual XLSX files?
Or do you have files that are instead using the ancient XLS format instead?
If you have actual XLS files so any of the files have multiple worksheets?
If so you will need to use some other tool to convert the sheets into something that SAS can read.
If you have XLSX files then the XLSX libref engine will let you get the column headers. Whether or not the variables get defined as the same type does not impact the value of the column headers. So if the variable types matter then you have a different issue than what you question says.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
They are actually XLS files.
They have sheet NAMES (as opposed to Sheet1) but each one only has a single sheet, so if there is some workaround there, let me know.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If they only have one sheet then just use proc import.
Example:
proc import datafile='file1.xls' dbms=xls out=dummy replace;
run;
proc contents data=dummy noprint out=contents;
run;
proc print data=contents;
var varnum name label;
run;
To aggregate the names over multiple XLS files you could make a macro that takes as input the filename and appends each new file to base table.
%macro xls_vars(filename);
proc import datafile=&filename dbms=xls out=dummy replace;
run;
proc contents data=dummy noprint out=contents;
run;
data this_file;
length filename $200 ;
filename=&filename;
set contents(keep=varnum name label);
run;
proc append base=all_files data=this_file force;
run;
%mend;Then call it once for each XLS file.
So if you have a dataset name FILES with a variable named FILENAME that has the list of XLS files you want read you could run this step to call the macro once for each file.
data _null_;
set files;
call execute(cats('%nrstr(%xls_vars)(',quote(trim(filename),"'"),')'));
run;
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
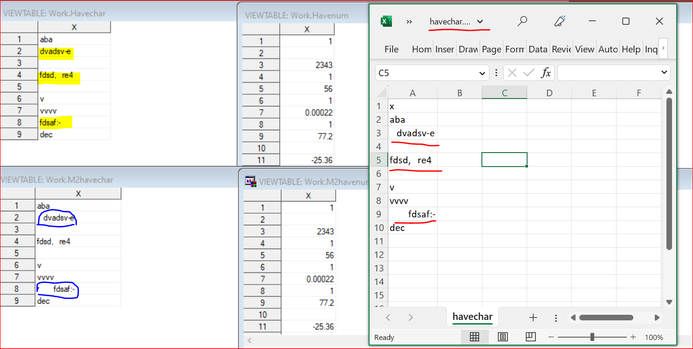
Hi:
Since I don't know what your data look like, so I created 2 excel files (havenum, havechar- X is defined as num and char ),
please see attached files.
Methods:
1. One of the approach is to convert excel files to CSV files-select CSV UTF-8(Comma Delimited).
then use PRO IMPORT. (Method 1 in the SAS code)
You may need to find a way to convert xls to CSV by using VBA code for a batch conversion.
2. To use ALLCHAR for SAS 9.4M5 users (Method 2 in the SAS code)
/*STEP1: Save the xls file to CSV file
To convert Excel to CSV file without losing data,
first, navigate to File and click on Save As.
From the Save As type dropdown, select CSV UTF-8(Comma Delimited). Click on Save.
This saves the CSV file without losing any characters*/
/*STEP2: proc import ,dbms=csv ,text file
Note: there is a new option but only available for SAS9.4,
https://documentation.sas.com/doc/en/pgmsascdc/9.4_3.5/proc/p12uk352fte2h1n1efh4r44dmxmp.htm*/
/* METHOD 1 */
PROC IMPORT OUT= havechar
DATAFILE="C:\havechar.csv"
DBMS=CSV
REPLACE;
guessingrows=33333;
GETNAMES=YES;
run;
PROC IMPORT OUT= havenum
DATAFILE="C:\havenum.csv"
DBMS=CSV
REPLACE;
guessingrows=3333;
GETNAMES=YES;
run;
/* METHOD 2 */
%let EFI_ALLCHARS=YES;
PROC IMPORT OUT= m2havechar
DATAFILE="C:\havechar.xlsx"
DBMS=xlsx;
run;
PROC IMPORT OUT= m2havenumm
DATAFILE="C:\havenum.xlsx"
DBMS=xlsx;
run;
%let EFI_ALLCHARS=no;
Output:
Note: It seems that Method 2 successfully keep the original format for characters- see the difference between yellow vs blue cell.
Method 1 (Yellow), X are aligned right , but Method 2(Blue) keeps the blanks
Reference Post: allchar option
https://communities.sas.com/t5/SASware-Ballot-Ideas/PROC-IMPORT-all-fields-as-character/idi-p/278415...
Add an ALLCHAR option to the PROC IMPORT statement -- to import all variables as character.
This should apply to external text files and to Excel files (considering CSV files to be text files)
SAS document:
https://documentation.sas.com/doc/en/pgmsascdc/9.4_3.5/proc/p12uk352fte2h1n1efh4r44dmxmp.htm
best wish,
purple
Learn how use the CAT functions in SAS to join values from multiple variables into a single value.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.
SAS Training: Just a Click Away
Ready to level-up your skills? Choose your own adventure.