- Home
- /
- Programming
- /
- Programming
- /
- Re: PROC SQL vs. Data Step Merge not getting same results
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I'm having trouble understanding why my proc sql and data step merge are not getting the same results. It seems to be off by one observation (I'm trying to convert my proc sql into a data step). Here is the full code:
data mydata;
infile datalines;
input list $ NDC discount;
datalines;
Nov 11 50
Dec 12 20
Nov 11 50
May 12 .
Mar 11 30
;
run;
data mydata2;
infile datalines;
input list $ NDC discount;
datalines;
Jan 11 40
Dec 12 20
Mar 10 50
May 12 .
Mar 11 30
;
run;
proc sql;
create table x1 as
select *
from mydata t1 left join mydata2 t2 on(t1.list=t2.list);
quit;
proc sort data=mydata;
by list;
run;
proc sort data=mydata2;
by list;
run;
data x2;
merge mydata(in=t1) mydata2;
by list;
if t1;
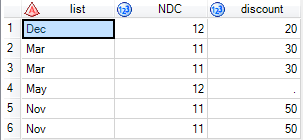
run;Results of x1:
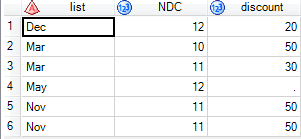
Results of x2:
The second observation from x1 is different from that of x2. Why is this? It must be something extremely simple - forgive me if I'm wasting your time.
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Because your variable names are the same in both data set. With a MERGE the last value read is the one that you will see in the output. WIth SELECT * in SQL the first instance of that variable is the one that is output if there is another variable with the same name then it is ignored.
Try this step and see if it doesn't match the SQL result.
data x3;
merge mydata2 mydata(in=t1);
by list;
if t1;
run;Since MYDATA is listed last the values of NDC and DISCOUNT from the MYDATA records will overwrite the values from the MYDATA2 records.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
In other words, why am I getting that observation from mydata2 when I specified "if t1".
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Since you are merging by LIST, IF T1 means "did this LIST value appear in T1?" If it did, the results of the merge appear in the final data set.
One of the issues involved in getting different results is the meaning of SELECT * from MYDATA. This brings in data values from MYDATA only, and brings in nothing from MYDATA2. The only way MYDATA2 gets used is to compare its LIST values to those in MYDATA. Which observation looks to you like it comes from MYDATA2?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Astounding "One of the issues involved in getting different results is the meaning of SELECT * from MYDATA. This brings in data values from MYDATA only, and brings in nothing from MYDATA2."
Then how come when I do this and select * in the proc sql at the end, all values from both datasets get brought in?
data mydata;
infile datalines;
input ID $ Country $ Code;
datalines;
A USA 228
B BGM 210
C CAN 200
;
run;
data mydata2;
infile datalines;
input ID $ State $ age;
datalines;
A WI 15
B CA 12
C MN 20
;
run;
proc sql;
create table want as
select *
from have t1 left join have2 t2 on(t1.ID=t2.ID);
quit;Is it because I'm now using different variables?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Because your variable names are the same in both data set. With a MERGE the last value read is the one that you will see in the output. WIth SELECT * in SQL the first instance of that variable is the one that is output if there is another variable with the same name then it is ignored.
Try this step and see if it doesn't match the SQL result.
data x3;
merge mydata2 mydata(in=t1);
by list;
if t1;
run;Since MYDATA is listed last the values of NDC and DISCOUNT from the MYDATA records will overwrite the values from the MYDATA2 records.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The log will give you answers. Merging or joining datasets that contain the same variables always gives peculiar results (accompanied by log messages in the case of SQL when using select *) and is generally a BAD IDEA.
While SQL only takes variables from one table, the data step overwrites values in the sequence in which observations are read from the contributing tables.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
But SQL does take variables from both tables... I'm not sure I understand. If you have two tables - lets say have multiple variables but they share one variable i ncommon and you do a left join on that, you will get all the other variables from the datasets when you use a select *
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Your problem with SQL is that you cannot create a SAS dataset with two variables that have the same name.
Try this code to see what is happening.
proc sql ;
select a.name,b.name
from sashelp.class a
inner join sashelp.class b
on a.name = b.name
;
create table test as
select a.name,b.name
from sashelp.class a
inner join sashelp.class b
on a.name = b.name
;
select * from test ;
quit;
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@JediApprentice wrote:
But SQL does take variables from both tables...
ONLY when they have different names.
Learn how use the CAT functions in SAS to join values from multiple variables into a single value.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.
SAS Training: Just a Click Away
Ready to level-up your skills? Choose your own adventure.