- Home
- /
- Programming
- /
- Programming
- /
- Re: Calculate a modified version of moving averages
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
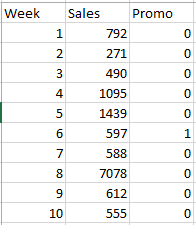
I have a data set which looks like this.
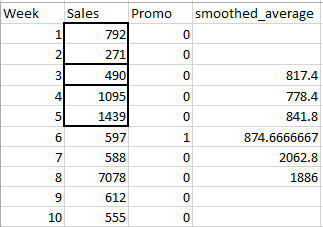
I want to calculate for every row, starting from row number three a moving average with window 5. For every row i, the window will have rows i-2, i-1, i, i+1, i+2. The desired output is like this.
So for week 3, The smoothed_average is a mean of the highlighted cells.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Use the CONVERT statement and the transformout=(cmovave 5) option in PROC EXPAND and do something like this
proc expand data=YourData;
id Week;
convert value=smoothed_average / transformout=(cmovave 5);
run;
This creates a Centered Moving Average of five observations (The two preceding, the present and the two next observations)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Next time write some code to make it as a table ,not picture. No one would like to type it for you ,if you want someone answer your question.
data have;
input week sales promo;
cards;
1 792 0
2 271 0
3 490 0
4 1095 0
5 1439 0
6 597 0
7 588 0
8 7078 0
;
run;
proc sql;
select * ,(select avg(sales) from have where week between a.week-2 and a.week+2) as avg
from have as a;
quit;- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If u don't have SAS/ETS you won't be able to use proc expand. Here is a data step approach that should work.
data want;
set have nobs=nobs;
if _N_ > 2 and _N_ <= nobs-2 then do; *Logic to only calculate a smoothed average when there are two prior rows as well as two following rows;
smoothed_average = Sales;
*Grab the preceding 2 and following 2 rows;
do i = -2, -1, 1, 2;
GetPoint = _N_ + i;
set have(keep=Sales Rename=(Sales=PriorSales)) point=GetPoint;
smoothed_average + PriorSales;
end;
smoothed_average = smoothed_average / 5;
end; else
smoothed_average = .;
drop i PriorSales;
run;
The third line may need to change depending on your actual data to start and stop calculating properly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
You want a size 5 window centered on the current observation.
PROC EXPAND is the way to go, assuming you have the sas/ets product. But if you don't, then this program will do:
data have;
input week sales promo;
cards;
1 792 0
2 271 0
3 490 0
4 1095 0
5 1439 0
6 597 0
7 588 0
8 7078 0
9 612 0
10 555 0
run;
data want (drop=leading_value);
merge have
have (firstobs=3 keep=sales rename=(sales=leading_value));
smoothed_average=ifn(_n_>=3,mean(lag2(sales),lag(sales),sales,lag(leading_value),leading_value),.);
if leading_value=. then smoothed_average=.;
run;
This program assumes there are no missing values for sales, which means "if leading_value=. then smoothed_average=.;" statement will prevent unwanted averages at the end of the data set.
The hash OUTPUT method will overwrite a SAS data set, but not append. That can be costly. Consider voting for Add a HASH object method which would append a hash object to an existing SAS data set
Would enabling PROC SORT to simultaneously output multiple datasets be useful? Then vote for
Allow PROC SORT to output multiple datasets
--------------------------
April 27 – 30 | Gaylord Texan | Grapevine, Texas
Registration is open
Walk in ready to learn. Walk out ready to deliver. This is the data and AI conference you can't afford to miss.
Register now and lock in 2025 pricing—just $495!
Learn how use the CAT functions in SAS to join values from multiple variables into a single value.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.
SAS Training: Just a Click Away
Ready to level-up your skills? Choose your own adventure.