- Home
- /
- Programming
- /
- SAS Procedures
- /
- Re: Proc expand & Data step: Standard deviation and Correlation
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Good days to all,
I have a dataset (as attached) with the following variables;
gvkey = company identification code
fyear = financial year
IB_LAT = earnings
CFO_LAT = cash flows
ACCR_LAT = accruals
I wish to calculate the following variables:
SMTH1 is the standard deviation of earnings (IB_LAT) divided by the standard deviation of cash flows (CFO_LAT), where standard deviations are calculated using a minimum of three and maximum of five years of data (t-4 to t); SMTH1 is multiplied by negative one so that larger values, i.e., values closer to zero, represent smoother earnings.
SMTH2 is defined as the correlation between the cash flows (CFO_LAT) and total accruals (ACCR_LAT), correlations are calculated using a minimum of three and maximum of five years of data (t-4 to t); SMTH2 is multiplied by negative one so that larger values, i.e., values closer to one, represent smoother earnings.
I intend to use either DATA step or Proc Expand to calculate the variables. However, I have no idea how to ensure I have at least 3 years of data available to fulfill such definitions.
*t-4 to t = 5 years = lag4(x), lag3(x), lag2(x), lag1(x), x.
Is the option for "correlation" available in proc expand? I found a blog that is close to my query:
Rolling Correlation Window [Archive] - Statistics Help @ Talk Stats Forum
By referring to proc expand user guide: SAS/ETS(R) 9.3 User's Guide, the following commands are available, I'm not sure to what extend these codes can be applied to my case:
> number | Missing value if |
>= number | Missing value if |
= number | Missing value if |
| Missing value if |
< number | Missing value if |
<= number | Missing value if |
Thank you and hope to get any help.
Regards,
mspak
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi all,
I tried out the solution for my SMTH1 answer but yet to get the answer for SMTH2.
My SAS code to calculate SMTH1 is as follows:
PROC SORT DATA= final.test2 OUT=TEST NODUPKEY;
BY GVKEY FYEAR; RUN;
proc expand data=TEST OUT=TEST1 method=none;
by GVKEY;
convert IB_lat = lag1_IB / transformout = (lag 1);
convert IB_lat = lag2_IB / transformout = (lag 2);
convert IB_lat = lag3_IB / transformout = (lag 3);
convert IB_lat = lag4_IB / transformout = (lag 4);
convert cfo_lat = lag1_CFO / transformout = (lag 1);
convert cfo_lat = lag2_CFO / transformout = (lag 2);
convert cfo_lat = lag3_CFO / transformout = (lag 3);
convert cfo_lat = lag4_CFO / transformout = (lag 4);
run;
DATA TEST2; SET TEST1;
SD_IB = STD(IB_lat, lag1_IB, lag2_IB, lag3_IB, lag4_IB);
iF MISSING (IB_lat) THEN miss_ib = 1; else miss_ib = 0;
iF MISSING (lag1_IB) THEN miss_lag1_IB = 1; else miss_lag1_IB = 0;
iF MISSING (lag2_IB) THEN miss_lag2_IB = 1; else miss_lag2_IB = 0;
iF MISSING (lag3_IB) THEN miss_lag3_IB = 1; else miss_lag3_IB = 0;
iF MISSING (lag4_IB) THEN miss_lag4_IB = 1; else miss_lag4_IB = 0;
totalmissIB = SUM(miss_ib, miss_lag1_IB, miss_lag2_IB , miss_lag3_IB, miss_lag4_IB);
IF totalmissIB > 2 THEN SD_IB = .;
SD_CFO = STD(cfo_lat, lag1_CFO, lag2_CFO, lag3_CFO, lag4_CFO);
iF MISSING (CFO_lat) THEN miss_ib = 1; else miss_ib = 0;
iF MISSING (lag1_CFO) THEN miss_lag1_CFO = 1; else miss_lag1_CFO = 0;
iF MISSING (lag2_CFO) THEN miss_lag2_CFO = 1; else miss_lag2_CFO = 0;
iF MISSING (lag3_CFO) THEN miss_lag3_CFO = 1; else miss_lag3_CFO = 0;
iF MISSING (lag4_CFO) THEN miss_lag4_CFO = 1; else miss_lag4_CFO = 0;
totalmissCFO = SUM(miss_ib, miss_lag1_CFO, miss_lag2_CFO , miss_lag3_CFO, miss_lag4_CFO);
IF totalmissCFO > 2 THEN SD_CFO = . ;
SMTH1 = -SD_IB/SD_CFO;
RUN;
Hope this can provide some insight to the solution of smth2.
Thank you.
Regards,
mspak
Learn the difference between classical and Bayesian statistical approaches and see a few PROC examples to perform Bayesian analysis in this video.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.
SAS Training: Just a Click Away
Ready to level-up your skills? Choose your own adventure.

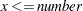 , else x
, else x 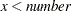 , else x
, else x 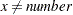 , else x
, else x 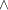 = number
= number 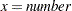 , else x
, else x 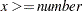 , else x
, else x 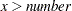 , else x
, else x 

