- Home
- /
- Programming
- /
- SAS Procedures
- /
- How to insert a row/observation within a table?
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
How to insert a row/observation within a table?
And by the meantime, I also filled the whole table with observations for the whole time span.
Say, in the example, for each ID, I want to creat the state for every time (1 2 3 4 5 6 7). If there is a new state, just follow it. If there is no new state, follow the last state observed.
I have searched some codes, but they all add new rows to the end of the table. Thanks you for your help in advance.
data have;
input ID $ time $ state;
cards;
a 1 23
a 5 25
b 1 65
b 2 33
b 7 28
c 2 13
;
run;
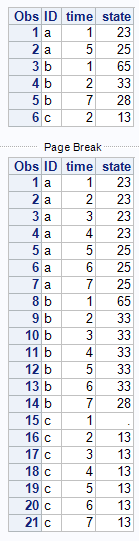
So the data output I get in mind is that:
a 1 23
a 2 23
a 3 23
a 4 23
a 5 25
a 6 25
a 7 25
b 1 65
b 2 33
b 3 33
b 4 33
b 5 33
b 6 33
b 7 28
c 1 .(no state observed yet)
c 2 13
c 3 13
c 4 13
c 5 13
c 6 13
c 7 13
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
This is the method I like to use.
data have;
input ID $ time state;
cards;
a 1 23
a 5 25
b 1 65
b 2 33
b 7 28
c 2 13
;;;;
run;
proc print;
run;
data class;
do time=1 to 7;
output;
end;
run;
proc summary nawy classdata=class data=have;
by id;
class time;
output out=framed(drop=_:) idgroup(out(state)=);
run;
data filled;
update framed(obs=0) framed;
by id;
output;
run;
proc print;
run;- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Your first issue is the missing levels - which is a commonly asked question.
http://www.pharmasug.org/proceedings/2012/CC/PharmaSUG-2012-CC26.pdf
Does your data have an observation for every level at some point? If so, Proc Freq with SPARSE option can help you build your table.
The second will have to do with retaining previous values which you can do in a data step.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
This is the method I like to use.
data have;
input ID $ time state;
cards;
a 1 23
a 5 25
b 1 65
b 2 33
b 7 28
c 2 13
;;;;
run;
proc print;
run;
data class;
do time=1 to 7;
output;
end;
run;
proc summary nawy classdata=class data=have;
by id;
class time;
output out=framed(drop=_:) idgroup(out(state)=);
run;
data filled;
update framed(obs=0) framed;
by id;
output;
run;
proc print;
run;Learn the difference between classical and Bayesian statistical approaches and see a few PROC examples to perform Bayesian analysis in this video.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.
SAS Training: Just a Click Away
Ready to level-up your skills? Choose your own adventure.