- Home
- /
- SAS Communities Library
- /
- Loading CAS from an Avro Binary file with complex data types
- RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Loading CAS from an Avro Binary file with complex data types
- Article History
- RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hadoop is the most commonly used data storage and processing environment in Big Data world. Apart from storing plain text data formats, users may choose to store data in serialized formats with complex data types. One of the most widely used data serialization formats is Avro, which enables users to store nested data structures with complex data types like STRUCT, ARRAY, Maps etc. An Avro data file with complex data types can be created by various applications like Hive, SPARK, Impala, Tez, Pig, etc.
Now, as a SAS user we ask the question, "Out of the box, can SAS directly read an Avro binary data file with complex data types to load into CAS?" Answer is no! SAS cannot directly read an Avro binay data file, even if you try using PROC HDMD to generate a schema for the file (without something like a custom reader).
SAS can, however, read an Avro file via Hive (when an Avro data file schema is registered in Hive-Catalog). For Avro files with complex data types, the user needs to parse the complex data into multiple separate columns at hive before reading into SAS. To do this, the user may create a Hive view with parsed columns on top of the Avro Hive table to read each data element as separate columns from nested complex data.
The following steps describe loading CAS with an Avro data file with complex data type (STRUCT) using a Hive view.
-
Retrieve the schema from a Binary Avro data file.
The Avro data file contains both Schema and actual data values. The Avro data file header contains the schema. Most hadoop distributions come with an application called “avro-tools” which can be used to extract Avro file schemas. (If an Avro data file is too big to move around for schema extraction, try using “head " statement.)
The following Unix statement extracts the schema from the sample.avro data file and places the schema into the sample.avsc file.
If you don’t have ‘avro-tools’ in your hadoop environment, you can download the compatible ‘avro-tools-XXXX.jar’ file from apache site and extract schema as follows.$ avro-tools getschema sample.avro > sample.avsc$ java -jar ~/avro-tools-X.X.X.jar getschema sample.avro > sample.avsc -
Place the Avro data and schema files into an HDFS folder (non /user/hive/warehouse location).
Use the following statement (or equivalent) to place the Avro data file and corresponding extracted schema file into an HDFS folder where the user ‘hive’ has access to register it in Hive-Catalog.$ hadoop fs -put sample.avsc /user/cloud-user/avro_schema/ $ hadoop fs -put sample.avro /user/cloud-user/avro_data/ $ hadoop fs -ls -R /user/cloud-user drwxr-xr-x - cloud-user hive 0 2018-05-07 16:26 /user/cloud-user/avro_data -rw-r--r-- 3 cloud-user hive 754261 2018-05-07 16:26 /user/cloud-user/avro_data/sample.avro drwxr-xr-x - cloud-user hive 0 2018-05-07 16:25 /user/cloud-user/avro_schema -rw-r--r-- 3 cloud-user hive 10933 2018-05-07 16:25 /user/cloud-user/avro_schema/sample.avsc -
Create a Hive table based on the Avro data and schema files.
Use the "create external table" statement to register the Avro schema with Data file into Hive-Catalog. Note the SERDE, INPUTFORMAT, OUTPUTFORMAT, LOCATION, and TABLEPROPERTIES options used. The option values for these parameters will vary depending upon the values used while creating the Avro file.CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE avro_sample_table ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.avro.AvroSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.avro.AvroContainerInputFormat' OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.avro.AvroContainerOutputFormat' LOCATION '/user/cloud-user/avro_data' TBLPROPERTIES('avro.schema.url'='hdfs://servername.xxx.xxx:8020/user/cloud-user/avro_schema/sample.avsc'); -
Verify the hive table structure and access of data at hive prompt.
Notice the hive table has only two columns, Key and Value. The ‘Value’ column is a complex data type STRUCT. While SAS/ACCESS treats the STRUCT as a CHAR(32K) column, the SAS Data Connector for Hadoop does not support the STRUCT data type (without a custom reader).hive> desc avro_sample_table ; OK key string value struct'<'siteean:string,siteplgkey:string,countrycode:string, aclgeskey:string,sitemaincode:string,sitefinkey:string,sitedesc:string,address1:string.... -
hive> select * from avro_sample_table limit 1; OK 3020180258104 {"siteean":"3020180258104","siteplgkey":"","countrycode":"xx"..........} Time taken: 0.144 seconds, Fetched: 1 row hive> -
Create a Hive View to parse the complex data type(s).
You can use the Avro schema file (XX.avsc) as a template for starting your Hive view. Copy the file and add the required statements (e.g. "create view"). Pay special attention to any nested column in the table/view. In this example, geoloctype, geox and geoy are nested columns and accordingly it’s addressed to read the actual value. There is no automated mechanism for generating the view statement. You have to manually verify that all columns are addressed properly.
Arrays and other repeating structures (e.g. an entity with multiple phone numbers) will need to be parsed into a flat structure (e.g. Phone1, Phone2, Phone3, …).create view avro_sample_view as select key, value.siteEan, value.sitePlgKey, value.countryCode, value.aclGesKey, ...value.geoLocation.geoLocType, value.geoLocation.geoX, value.geoLocation.geoY, value.createDate, value.deleteDate, …… …. value.siteIntDesc from avro_sample_table;
Here we store our view code in a file, ‘hv_view.sql’, and invoke the hive application to create view at hive.$ hive -f hv_view.sql -
Load the Hive view using the DATA Connector and Accelerator.
75 75 ! load casdata="avro_sample_view" casout="avro_sample_view" 76 outcaslib="HiveEP" incaslib="HiveEP" ; NOTE: Executing action 'table.loadTable'. NOTE: Performing parallel LoadTable action using SAS Data Connect Accelerator for Hadoop. NOTE: Cloud Analytic Services made the external data from avro_sample_view available as table AVRO_SAMPLE_VIEW in caslib HiveEP. NOTE: Action 'table.loadTable' used (Total process time):Table structure of the CAS table loaded from the Hive view, Avro_view:
Note 1: Separate columns for each data element from the complex STRUCT data type.
Note 2: All STRING data type from Avro_Hive table converted into VARCHAR by CAS.
Observations:
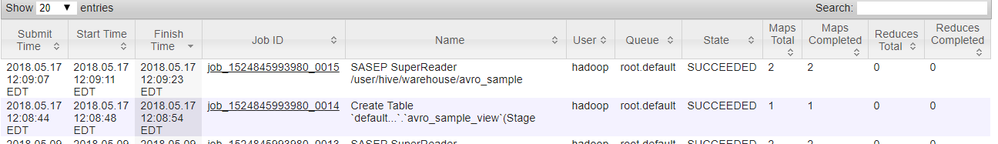
On the Hadoop cluster, the Data load to CAS job executes in two steps. First, it stages the data in a temporary location, then SAS EP feeds the data to CAS.
April 27 – 30 | Gaylord Texan | Grapevine, Texas
Registration is open
Walk in ready to learn. Walk out ready to deliver. This is the data and AI conference you can't afford to miss.
Register now and save with the early bird rate—just $795!
SAS AI and Machine Learning Courses
The rapid growth of AI technologies is driving an AI skills gap and demand for AI talent. Ready to grow your AI literacy? SAS offers free ways to get started for beginners, business leaders, and analytics professionals of all skill levels. Your future self will thank you.
- Find more articles tagged with:
- GEL