- Home
- /
- Analytics
- /
- Stat Procs
- /
- testing for a negative correlation between 2 dependent variables in a ...
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Steve, I was doing a mistake, because I was using the residual option with the beta and the binomial dist, and for distributions where the mean and variance are functionally related you should not use the residual option. So now I get negative values with the binomial dist for the prop of healthy vs prop diseased eggs ![]() and Gener. Chi-Square / DF=0.08
and Gener. Chi-Square / DF=0.08
| 1 | 1.0000 | -337E-24 | 9.25E-26 | -148E-31 | 5.01E-33 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1.0000 | -84E-22 | 2.3E-24 | -369E-30 | 1.25E-31 | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | -337E-24 | 1.0000 | -346E-24 | 5.55E-26 | -187E-31 | |||||||||||||||
| 4 | -84E-22 | 1.0000 | -863E-23 | 1.38E-24 | -467E-30 | |||||||||||||||
| 5 | 9.25E-26 | -346E-24 | 1.0000 | -271E-24 | 9.18E-26 | |||||||||||||||
| 6 | 2.3E-24 | -863E-23 | 1.0000 | -676E-23 | 2.29E-24 | |||||||||||||||
| 7 | -148E-31 | 5.55E-26 | -271E-24 | 1.0000 | -262E-24 | |||||||||||||||
| 8 | -369E-30 | 1.38E-24 | -676E-23 | 1.0000 | -653E-23 | |||||||||||||||
| 9 | 5.01E-33 | -187E-31 | 9.18E-26 | -262E-24 | 1.0000 | |||||||||||||||
| 10 | 1.25E-31 | -467E-30 | 2.29E-24 | -653E-23 | 1.0000 | |||||||||||||||
| 11 | 1.0000 | -301E-24 | 6.43E-26 | -162E-31 | 4.12E-33 | |||||||||||||||
| 12 | 1.0000 | -749E-23 | 1.6E-24 | -404E-30 | 1.03E-31 | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | -301E-24 | 1.0000 | -342E-24 | 8.62E-26 | -219E-31 | |||||||||||||||
| 14 | -749E-23 | 1.0000 | -852E-23 | 2.15E-24 | -546E-30 | |||||||||||||||
| 15 | 6.43E-26 | -342E-24 | 1.0000 | -329E-24 | 8.37E-26 | |||||||||||||||
| 16 | 1.6E-24 | -852E-23 | 1.0000 | -82E-22 | 2.08E-24 | |||||||||||||||
| 17 | -162E-31 | 8.62E-26 | -329E-24 | 1.0000 | -376E-24 | |||||||||||||||
| 18 | -404E-30 | 2.15E-24 | -82E-22 | 1.0000 | -936E-23 | |||||||||||||||
| 19 | 4.12E-33 | -219E-31 | 8.37E-26 | -376E-24 | 1.0000 | |||||||||||||||
| 20 | 1.03E-31 | -546E-30 | 2.08E-24 | -936E-23 | 1.0000 |
Although there is no significant interaction including eggtype in the table for fixed effects.
Thanks Steve!!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
But you aren't getting negative values. The off diagonal values are all zeroes to the extent of machine accuracy, and may show as almost anything.
So to look at counts and proportions in the same analysis, look at Example 44.5 Joint Modeling of Binary and Count Data (may have a different example number, depending on version of SAS/STAT. This is for 13.2). In particular, take a look at the very last set of code for a marginally correlated error model.
Steve Denham
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I see. Anyhow, when I plot the data, it doesn´t look like there is really a neg corr with log and logit transformed counts and proportions, eventhough the oscillations seems to be opposite
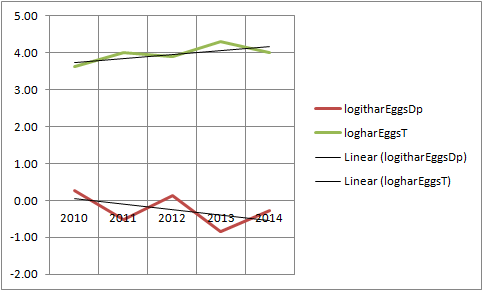
Thank you so much for all your great help Steve!
Caroline
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi again Steve,
I found a correlation that seems to be positive, but how to get the p-values under each corr coefficient in order to determine if they are significant? Is there a statement that I can include in my code?
Proc glimmix data=one;
class nem blk year eggtype;
model Eggs= eggtype|nem|year/dist=lognormal ddfm=kr;
random intercept/subject=blk;
random year/residual subject=blk*nem type=ar(1) group=eggtype vcorr;
run;
Thank you dear Steve!
Caroline
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Not in GLIMMIX. I think the best you can do will be to export to a dataset, apply Fisher's transformation (hyperbolic arctangent) and get a z-score, using the residual degrees of freedom, rather than the n - 3 for the standard analysis.
Steve Denham
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
You have a solution for everything Steve!
Thank you so much for all your wonderful help!!
Caroline
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Not really--I've just been doing a lot of this stuff for a long time.
Steve Denham
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I tried healthy eggs with disease eggs. Significant interactions including eggtype, but still no negative values. I also compared proportion of healthy eggs with proportion of disease eggs, but no negative values.
I would appreciate if you could have a look, maybe I am doing something wrong. (harEggsT means he number of total eggs. I also divided 4 because I need the numbers in 100g soil and he raw data is in 400g)
data one;
input nem$ blk$ year eggtype$ harEggs harEggsT;
harEggs=harEggs/4;
harEggs=harEggs+1;
harEggsT=harEggsT/4;
harEggsT=harEggsT+1;
harPerEggs=100*harEggs/harEggsT;
cards;
Chav A 2010 healthy 1400 8700
Chav A 2010 diseased 7300 8700
Chav A 2011 healthy 27375 35250
Chav A 2011 diseased 7875 35250
Chav A 2012 healthy 9700 27900
Chav A 2012 diseased 18200 27900
Chav A 2013 healthy 60625 68875
Chav A 2013 diseased 8250 68875
Chav A 2014 healthy 19350 34425
Chav A 2014 diseased 15075 34425
Chav B 2010 healthy 3000 10800
Chav B 2010 diseased 7800 10800
Chav B 2011 healthy 17100 21700
Chav B 2011 diseased 4600 21700
Chav B 2012 healthy 11625 28275
Chav B 2012 diseased 16650 28275
Chav B 2013 healthy 71750 81500
Chav B 2013 diseased 9750 81500
Chav B 2014 healthy 25500 46800
Chav B 2014 diseased 21300 46800
Chav C 2010 healthy 27200 36000
Chav C 2010 diseased 8800 36000
Chav C 2011 healthy 44250 66500
Chav C 2011 diseased 22250 66500
Chav C 2012 healthy 13500 26500
Chav C 2012 diseased 13000 26500
Chav C 2013 healthy 82800 97650
Chav C 2013 diseased 14850 97650
Chav C 2014 healthy 29400 38300
Chav C 2014 diseased 8900 38300
Chav D 2010 healthy 5600 22400
Chav D 2010 diseased 16800 22400
Chav D 2011 healthy 43500 53100
Chav D 2011 diseased 9600 53100
Chav D 2012 healthy 17800 43900
Chav D 2012 diseased 26100 43900
Chav D 2013 healthy 62200 70600
Chav D 2013 diseased 8400 70600
Chav D 2014 healthy 35125 47875
Chav D 2014 diseased 12750 47875
Delm A 2010 healthy 800 12600
Delm A 2010 diseased 11800 12600
Delm A 2011 healthy 2850 24750
Delm A 2011 diseased 21900 24750
Delm A 2012 healthy 9150 34200
Delm A 2012 diseased 25050 34200
Delm A 2013 healthy 21500 30000
Delm A 2013 diseased 8500 30000
Delm A 2014 healthy 8750 16850
Delm A 2014 diseased 8100 16850
Delm B 2010 healthy 7000 46800
Delm B 2010 diseased 39800 46800
Delm B 2011 healthy 28000 62000
Delm B 2011 diseased 34000 62000
Delm B 2012 healthy 12400 41200
Delm B 2012 diseased 28800 41200
Delm B 2013 healthy 28350 37275
Delm B 2013 diseased 8925 37275
Delm B 2014 healthy 50300 72100
Delm B 2014 diseased 21800 72100
Delm C 2010 healthy 17250 55050
Delm C 2010 diseased 37800 55050
Delm C 2011 healthy 44700 88650
Delm C 2011 diseased 43950 88650
Delm C 2012 healthy 9400 51700
Delm C 2012 diseased 42300 51700
Delm C 2013 healthy 54375 89750
Delm C 2013 diseased 35375 89750
Delm C 2014 healthy 28200 56700
Delm C 2014 diseased 28500 56700
Delm D 2010 healthy . .
Delm D 2010 diseased . .
Delm D 2011 healthy . .
Delm D 2011 diseased . .
Delm D 2012 healthy . .
Delm D 2012 diseased . .
Delm D 2013 healthy . .
Delm D 2013 diseased . .
Delm D 2014 healthy . .
Delm D 2014 diseased . .
Proc glimmix data=one;
harPerEggsp=harPerEggs/100;
class nem blk year eggtype;
model harPerEggsp= eggtype|nem|year/dist=beta ddfm=kr;
random intercept/subject=blk;
random year/residual subject=blk*nem type=ar(1) group=eggtype vcorr;
run;
Thank you very much Steve!!
- « Previous
-
- 1
- 2
- Next »
Don't miss out on SAS Innovate - Register now for the FREE Livestream!
Can't make it to Vegas? No problem! Watch our general sessions LIVE or on-demand starting April 17th. Hear from SAS execs, best-selling author Adam Grant, Hot Ones host Sean Evans, top tech journalist Kara Swisher, AI expert Cassie Kozyrkov, and the mind-blowing dance crew iLuminate! Plus, get access to over 20 breakout sessions.
ANOVA, or Analysis Of Variance, is used to compare the averages or means of two or more populations to better understand how they differ. Watch this tutorial for more.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.



