- Home
- /
- Analytics
- /
- Stat Procs
- /
- help with intepretation of npar1way procedure (Wilcoxon's score)
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi all,
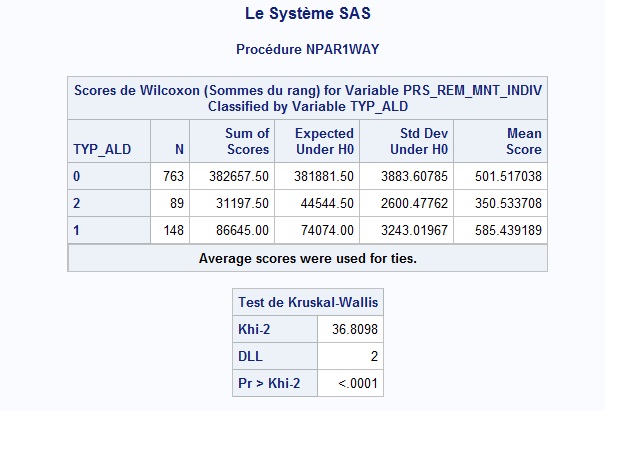
I have a sample of 1000 individuals divided in three groups : individuals where TYP_ALD=0, individuals where TYP_ALD=1, and individuals where TYP_ALD=2. For each of them I have an other variable called PRS_REM_MNT_INDIV which give me the amount that their insurance paid for them to cover their healthcare. My goal is to prove that this amount depends on what group you belong to (in other words, it will cost the insurance a lot more if your type of ALD is 0 for instance). I am far from having the normality satisfied so I've decided to use non-parametric test and so the Wilcoxon analysis. Here's what I've got in output using the npar1way procedure :
The Kruskal-Wallis test makes things pretty clear, however I'd also like to use the Wilcoxon's score table. Problem is I don't understand how the column 'Expected Under H0' is obtained. Can someone give me a hint on that and tell me how I can use this to prove my point?
Thank you all
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The K-W test uses ranks. You have 1000 observations, so the expected (median) rank is 500.5.
The null hypothesis is that the median is independent of the categories.
Under the null hypothesis, the expected rank for Type=0, which has 763 observations, is 763*500.5 = 381881.5 .
Under the null hypothesis, the expected rank for Type=2, which has 89observations, is 89*500.5 = 44544.5.
etc
For your data, it looks like the cost for Type=0 is about the same as expected under H0. However, payments for Type=2 is less than expected and payments for Type=1 is more than expected.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The K-W test uses ranks. You have 1000 observations, so the expected (median) rank is 500.5.
The null hypothesis is that the median is independent of the categories.
Under the null hypothesis, the expected rank for Type=0, which has 763 observations, is 763*500.5 = 381881.5 .
Under the null hypothesis, the expected rank for Type=2, which has 89observations, is 89*500.5 = 44544.5.
etc
For your data, it looks like the cost for Type=0 is about the same as expected under H0. However, payments for Type=2 is less than expected and payments for Type=1 is more than expected.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Don't miss out on SAS Innovate - Register now for the FREE Livestream!
Can't make it to Vegas? No problem! Watch our general sessions LIVE or on-demand starting April 17th. Hear from SAS execs, best-selling author Adam Grant, Hot Ones host Sean Evans, top tech journalist Kara Swisher, AI expert Cassie Kozyrkov, and the mind-blowing dance crew iLuminate! Plus, get access to over 20 breakout sessions.
ANOVA, or Analysis Of Variance, is used to compare the averages or means of two or more populations to better understand how they differ. Watch this tutorial for more.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.