- Home
- /
- Programming
- /
- Programming
- /
- Re: Write SAS Time fields to Excel - loses time format
- RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I have a SAS file with field named MYTIME which is Numeric and TIME. format associated. I want to write this to Excel, letting a co-worker edit some other fields, then read back into SAS. Problem is importing back into SAS, MYTIME is assigned TEXT type.
To write from SAS to Excel, and make sure format of MYTIME is kept as a time in Excel, I use:
ods excel file="myfile.xlsx";
proc print data=mydata;
var A B C;
var MYTIME / style(data)={tagattr='format:h:mm'};
run;
ods excel close;When I open Excel, it has correctly assigned a format of h:mm to the MYTIME column, so that looks good, but when I re-import the Excel file into SAS using this code...
proc import file="myfile.xlsx" dbms=xlsx out=test_read replace; run;... MYTIME now is type TEXT with format $8., not NUMERIC with TIME. format!
If I build an Excel file from scratch and enter a time into a cell, it correctly imports to SAS using PROC IMPORT code above, so something different is happening when I create the Excel file via SAS, but what?
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @bnawrocki , @Tom & @Patrick
There is a workaround so you can get your code working in M7 (Win and Linux) while you wait for a hotfix.
I added a step to Tom's code to convert the SAS time to an Excel time and remove the TIME Format from the variable. Then it works.
data test;
do hour=1 to 5 ;
time=hour*60*60 ;
output;
end;
format time time8.;
run;
* Step added to fix problem;
* Format statement placed before Set statement to remove the existing time format;
data test;
format time 8.;
set test;
time = time/86400;
run;
%let fname=%sysfunc(pathname(work))/example1.xlsx;
ods excel file="&fname" options (sheet_name='Sheet1');
proc print data=test noobs;
var hour;
var time / style(data)={tagattr='format:h:mm'};
run;
ods excel close ;
libname x xlsx "&fname";
proc contents data=x._all_;
run;
proc import file="&fname" dbms=xlsx out=test_read replace;
run;
proc contents data=test_read ;
run;
- And I am aware that using the same data set as input and output isn't best practice, but I took the liberty here to avoid making any changes in Tom's code.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks, ChrisNZ. However, I already tried the FORMAT statement for the MYTIME variable - that was the first version of my SAS code. However, the results are the same - when I read it back into SAS from Excel, PROC IMPORT sets MYTIME to text. In Excel, the MYTIME cells look OK, but are formatted as "Custom: #######0".
I'll try a couple other approaches today - PROC REPORT and PROC EXPORT.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
It works fine for me. Try to see what differs between your process and this one:
filename XL "myfile.xlsx";
ods excel file=XL;
proc print data=SASHELP.CLASS noobs;
var NAME SEX;
var AGE / style(data)={tagattr='format:h:mm'};
format AGE time.;
run;
ods excel close;
proc import file=XL dbms=xlsx out=READ replace;
proc print data=READ; run;| Obs | Name | Sex | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alfred | M | 0:00:14 |
| 2 | Alice | F | 0:00:13 |
| 3 | Barbara | F | 0:00:13 |
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@ChrisNZ Using your code I believe the challenge the OP raises is the data type of Age becoming character instead of numeric.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @bnawrocki
The trick here is to convert the Time Value to something Excel understands before writing data to Excel.
A Time Value is represented in Excel as a fraction of a day, but in SAS it is a number of seconds. So - given the input is a SAS Time Value - the SAS Time Value,should be divided by 86400 (the number of seconds in a day) to get the fraction. Then everything works
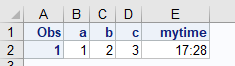
data mydata;
a = 1; b=2; c=3;
textvar = 'anyvalue';
mytime = '17:28:00't;
mytime = mytime/86400;
run;
ods excel file="c:\temp\test.xlsx";
proc print data=mydata;
var A B C;
var MYTIME / style(data)={tagattr='format:h:mm'};
run;
ods excel close;
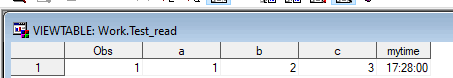
proc import file="c:\temp\test.xlsx" dbms=xlsx out=test_read replace;
run;Excel:
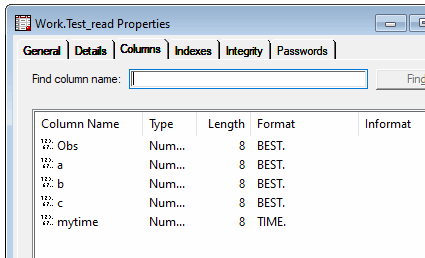
SAS Import:
SAS data set attributes:
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I cannot recreate your issue. Are you using an older version of SAS where ODS EXCEL is experimental? Check the version (including the M# ).
1460 %put &=sysvlong; SYSVLONG=9.04.01M5P091317
Did you modify the XLSX file with Excel before trying to read it?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
It doesn't seem to be a version issue. I use SAS 9.04.01M7P080520, and I get the same result as @bnawrocki when I run the posted code. The Time variable is imported from the XLSX file as a text.
I and I have tried running the code on a Windows X64_10Pro platform and also on a Red Hat Linux version 7.9 with the same result:
152 proc import file="/sasdata/udvk/work/test.xlsx" dbms=xlsx out=test_read replace;
153 run;
NOTE: VARCHAR data type is not supported by the V9 engine. Variable mytime has been converted
to CHAR data type.
NOTE: The import data set has 1 observations and 5 variables.
NOTE: WORK.TEST_READ data set was successfully created.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Seems to be a bug introduced in 9.4m6.
This code works fine in 9.4m5 on both Windows and Unix. But fails in m6 and m7 on Unix.
data test;
do hour=1 to 5 ;
time=hour*60*60 ;
output;
end;
format time time8.;
run;
%let fname=%sysfunc(pathname(work))/example1.xlsx;
ods excel file="&fname" options (sheet_name='Sheet1');
proc print data=test noobs;
var hour;
var time / style(data)={tagattr='format:h:mm'};
run;
ods excel close ;
libname x xlsx "&fname";
proc contents data=x._all_;
run;
proc import file="&fname" dbms=xlsx out=test_read replace;
run;
proc contents data=test_read ;
run;Results:
>grep time m?.lst m5.lst:hour time m5.lst: Obs hour time m5.lst:2 time Num 8 TIME. time m5.lst:2 time Num 8 TIME. time m6.lst:hour time m6.lst: Obs hour time m6.lst:2 time Char 7 $7. $7. time m6.lst:2 time Char 7 $7. $7. time m7.lst:hour time m7.lst: Obs hour time m7.lst:2 time Char 7 $7. $7. time m7.lst:2 time Char 7 $7. $7. time
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
It also fails for Windows 9.4M7 workstation
Current version: 9.04.01M7P080520 Operating System: WX64_WKS.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I couldn't find any SAS or defect Note for this issue so raised a SAS TechSupport track. I'll post proceedings here once received.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Just as an update: This issue has now been raised with SAS R&D.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @bnawrocki , @Tom & @Patrick
There is a workaround so you can get your code working in M7 (Win and Linux) while you wait for a hotfix.
I added a step to Tom's code to convert the SAS time to an Excel time and remove the TIME Format from the variable. Then it works.
data test;
do hour=1 to 5 ;
time=hour*60*60 ;
output;
end;
format time time8.;
run;
* Step added to fix problem;
* Format statement placed before Set statement to remove the existing time format;
data test;
format time 8.;
set test;
time = time/86400;
run;
%let fname=%sysfunc(pathname(work))/example1.xlsx;
ods excel file="&fname" options (sheet_name='Sheet1');
proc print data=test noobs;
var hour;
var time / style(data)={tagattr='format:h:mm'};
run;
ods excel close ;
libname x xlsx "&fname";
proc contents data=x._all_;
run;
proc import file="&fname" dbms=xlsx out=test_read replace;
run;
proc contents data=test_read ;
run;
- And I am aware that using the same data set as input and output isn't best practice, but I took the liberty here to avoid making any changes in Tom's code.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
9.2M2 on Windows here. I obtain different results.
The variable is never seen as a string, but is imported as number of hours instead of number of minutes if the time format is not applied.
That's because the custom Excel format strips the seconds.
When the format is applied, all works as expected (hence my suggestion earlier). Successive versions seem to behave differently.
ods excel file="&wdir\myfile.xlsx";
proc print data=SASHELP.CLASS(obs=3) noobs;
var NAME SEX;
format AGE time.;
var AGE / style(data)={tagattr='format:hh:mm'};
run;
ods excel close;
proc import file="&wdir\myfile.xlsx" dbms=xlsx out=T replace; run;
proc print; run;
proc contents; run;
ods excel file="&wdir\myfile.xlsx";
proc print data=SASHELP.CLASS(obs=3) noobs;
var NAME SEX;
* format AGE time.; ******************************* format commented out;
var AGE / style(data)={tagattr='format:hh:mm'};
run;
ods excel close;
proc import file="&wdir\myfile.xlsx" dbms=xlsx out=T replace; run;
proc print; run;
proc contents; run;
| Name | Sex | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Joyce | F | 0:00:11 |
| Thomas | M | 0:00:11 |
| James | M | 0:00:12 |
| Obs | Name | Sex | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Joyce | F | 0:00:11 |
| 2 | Thomas | M | 0:00:11 |
| 3 | James | M | 0:00:12 |
| Engine/Host Dependent Information | |
|---|---|
| Data Set Page Size | 131072 |
| Number of Data Set Pages | 2 |
| Number of Data Set Repairs | 0 |
| Filename | K:\SASWORK\_TD9924_NZ8037SPSAS2003_\Prc2\t.sas7bdat |
| Release Created | 9.0401M2 |
| Host Created | X64_SRV12 |
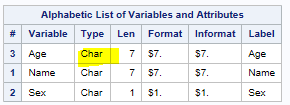
| Alphabetic List of Variables and Attributes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Variable | Type | Len | Format | Informat | Label |
| 3 | Age | Num | 8 | TIME. | Age | |
| 1 | Name | Char | 6 | $6. | $6. | Name |
| 2 | Sex | Char | 1 | $1. | $1. | Sex |
| Name | Sex | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Joyce | F | 11 |
| Thomas | M | 11 |
| James | M | 12 |
| Obs | Name | Sex | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Joyce | F | 264:00 |
| 2 | Thomas | M | 264:00 |
| 3 | James | M | 288:00 |
| Engine/Host Dependent Information | |
|---|---|
| Data Set Page Size | 131072 |
| Number of Data Set Pages | 2 |
| Number of Data Set Repairs | 0 |
| Filename | K:\SASWORK\_TD9924_NZ8037SPSAS2003_\Prc2\t.sas7bdat |
| Release Created | 9.0401M2 |
| Host Created | X64_SRV12 |
| Alphabetic List of Variables and Attributes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Variable | Type | Len | Format | Informat | Label |
| 3 | Age | Num | 8 | TIME. | Age | |
| 1 | Name | Char | 6 | $6. | $6. | Name |
| 2 | Sex | Char | 1 | $1. | $1. | Sex |
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
A hearty thank you to everyone who has responded to my question. The workaround code (see Accepted Solution) is working for me, so I'm happy!
April 27 – 30 | Gaylord Texan | Grapevine, Texas
Registration is open
Walk in ready to learn. Walk out ready to deliver. This is the data and AI conference you can't afford to miss.
Register now and lock in 2025 pricing—just $495!
Learn how use the CAT functions in SAS to join values from multiple variables into a single value.
Find more tutorials on the SAS Users YouTube channel.
SAS Training: Just a Click Away
Ready to level-up your skills? Choose your own adventure.